In October 2021, we discovered that the Magnitude exploit kit was testing out a Chromium exploit chain in the wild. This really piqued our interest, because browser exploit kits have in the past few years focused mainly on Internet Explorer vulnerabilities and it was believed that browsers like Google Chrome are just too big of a target for them.
About a month later, we found that the Underminer exploit kit followed suit and developed an exploit for the same Chromium vulnerability. That meant there were two exploit kits that dared to attack Google Chrome: Magnitude using CVE-2021-21224 and CVE-2021-31956 and Underminer using CVE-2021-21224, CVE-2019-0808, CVE-2020-1020, and CVE-2020-1054.
We’ve been monitoring the exploit kit landscape very closely since our discoveries, watching out for any new developments. We were waiting for other exploit kits to jump on the bandwagon, but none other did, as far as we can tell. What’s more, Magnitude seems to have abandoned the Chromium exploit chain. And while Underminer still continues to use these exploits today, its traditional IE exploit chains are doing much better. According to our telemetry, less than 20% of Underminer’s exploitation attempts are targeting Chromium-based browsers.
This is some very good news because it suggests that the Chromium exploit chains were not as successful as the attackers hoped they would be and that it is not currently very profitable for exploit kit developers to target Chromium users. In this blog post, we would like to offer some thoughts into why that could be the case and why the attackers might have even wanted to develop these exploits in the first place. And since we don’t get to see a new Chromium exploit chain in the wild every day, we will also dissect Magnitude’s exploits and share some detailed technical information about them.
Exploit Kit Theory
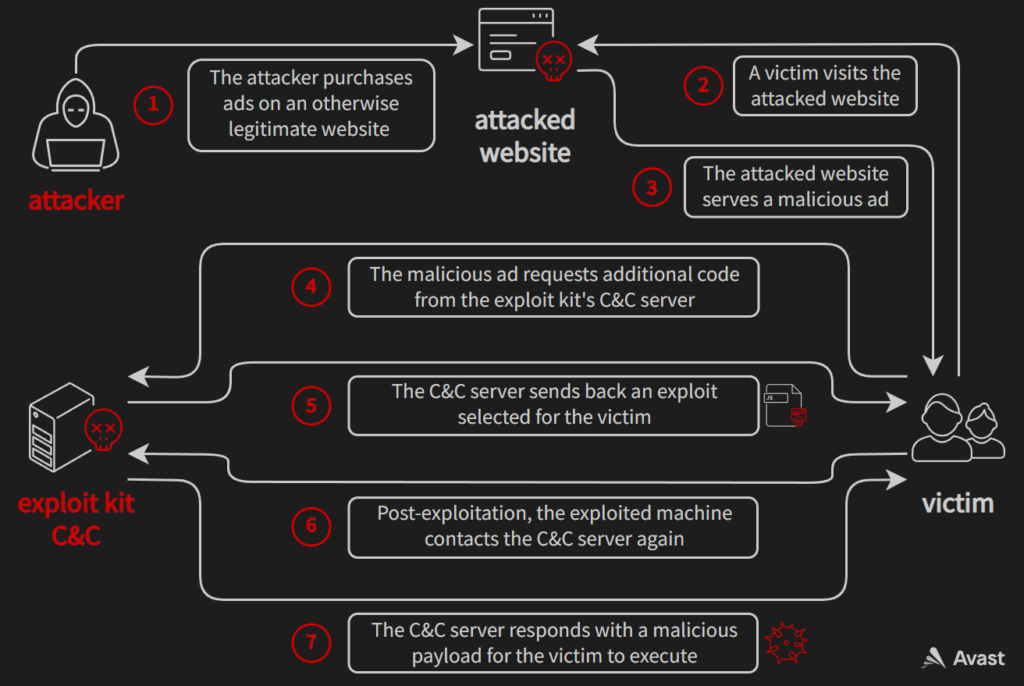
To understand why exploit kit developers might have wanted to test Chromium exploits, let’s first look at things from their perspective. Their end goal in developing and maintaining an exploit kit is to make a profit: they just simply want to maximize the difference between money “earned” and money spent. To achieve this goal, most modern exploit kits follow a simple formula. They buy ads targeted to users who are likely to be vulnerable to their exploits (e.g. Internet Explorer users). These ads contain JavaScript code that is automatically executed, even when the victim doesn’t interact with the ad in any way (sometimes referred to as drive-by attacks). This code can then further profile the victim’s browser environment and select a suitable exploit for that environment. If the exploitation succeeds, a malicious payload (e.g. ransomware or a coinminer) is deployed to the victim. In this scenario, the money “earned” could be the ransom or mining rewards. On the other hand, the money spent is the cost of ads, infrastructure (renting servers, registering domain names etc.), and the time the attacker spends on developing and maintaining the exploit kit.
The attackers would like to have many diverse exploits ready at any given time because it would allow them to cast a wide net for potential victims. But it is important to note that individual exploits generally get less effective over time. This is because the number of people susceptible to a known vulnerability will decrease as some people patch and other people upgrade to new devices (which are hopefully not plagued by the same vulnerabilities as their previous devices). This forces the attackers to always look for new vulnerabilities to exploit. If they stick with the same set of exploits for years, their profit would eventually reduce down to almost nothing.
So how do they find the right vulnerabilities to exploit? After all, there are thousands of CVEs reported each year, but only a few of them are good candidates for being included in an exploit kit. Weaponizing an exploit generally takes a lot of time (unless, of course, there is a ready-to-use PoC or the exploit can be stolen from a competitor), so the attackers might first want to carefully take into account multiple characteristics of each vulnerability. If a vulnerability scores well across these characteristics, it looks like a good candidate for inclusion in an exploit kit. Some of the more important characteristics are listed below.
- Prevalence of the vulnerability
The more users are affected by the vulnerability, the more attractive it is to the attackers. - Exploit reliability
Many exploits rely on some assumptions or are based on a race condition, which makes them fail some of the time. The attackers obviously prefer high-reliability exploits. - Difficulty of exploit development
This determines the time that needs to be spent on exploit development (if the attackers are even capable of exploiting the vulnerability). The attackers tend to prefer vulnerabilities with a public PoC exploit, which they can often just integrate into their exploit kit with minimal effort. - Targeting precision
The attackers care about how hard it is to identify (and target ads to) vulnerable victims. If they misidentify victims too often (meaning that they serve exploits to victims who they cannot exploit), they’ll just lose money on the malvertising. - Expected vulnerability lifetime
As was already discussed, each vulnerability gets less effective over time. However, the speed at which the effectiveness drops can vary a lot between vulnerabilities, mostly based on how effective is the patching process of the affected software. - Exploit detectability
The attackers have to deal with numerous security solutions that are in the business of protecting their users against exploits. These solutions can lower the exploit kit’s success rate by a lot, which is why the attackers prefer more stealthy exploits that are harder for the defenders to detect. - Exploit potential
Some exploits give the attackersSystem, while others might make them only end up inside a sandbox. Exploits with less potential are also less useful, because they either need to be chained with other LPE exploits, or they place limits on what the final malicious payload is able to do.
Looking at these characteristics, the most plausible explanation for the failure of the Chromium exploit chains is the expected vulnerability lifetime. Google is extremely good at forcing users to install browser patches: Chrome updates are pushed to users when they’re ready and can happen many times in a month (unlike e.g. Internet Explorer updates which are locked into the once-a-month “Patch Tuesday” cycle that is only broken for exceptionally severe vulnerabilities). When CVE-2021-21224 was a zero-day vulnerability, it affected billions of users. Within a few days, almost all of these users received a patch. The only unpatched users were those who manually disabled (or broke) automatic updates, those who somehow managed not to relaunch the browser in a long time, and those running Chromium forks with bad patching habits.
A secondary reason for the failure could be attributed to bad targeting precision. Ad networks often allow the attackers to target ads based on various characteristics of the user’s browser environment, but the specific version of the browser is usually not one of these characteristics. For Internet Explorer vulnerabilities, this does not matter that much: the attackers can just buy ads for Internet Explorer users in general. As long as a certain percentage of Internet Explorer users is vulnerable to their exploits, they will make a profit. However, if they just blindly targeted Google Chrome users, the percentage of vulnerable victims might be so low, that the cost of malvertising would outweigh the money they would get by exploiting the few vulnerable users. Google also plans to reduce the amount of information given in the User-Agent string. Exploit kits often heavily rely on this string for precise information about the browser version. With less information in the User-Agent header, they might have to come up with some custom version fingerprinting, which would most likely be less accurate and costly to manage.
Now that we have some context about exploit kits and Chromium, we can finally speculate about why the attackers decided to develop the Chromium exploit chains. First of all, adding new vulnerabilities to an exploit kit seems a lot like a “trial and error” activity. While the attackers might have some expectations about how well a certain exploit will perform, they cannot know for sure how useful it will be until they actually test it out in the wild. This means it should not be surprising that sometimes, their attempts to integrate an exploit turn out worse than they expected. Perhaps they misjudged the prevalence of the vulnerabilities or thought that it would be easier to target the vulnerable victims. Perhaps they focused too much on the characteristics that the exploits do well on: after all, they have reliable, high-potential exploits for a browser that’s used by billions. It could also be that this was all just some experimentation where the attackers just wanted to explore the land of Chromium exploits.
It’s also important to point out that the usage of Internet Explorer (which is currently vital for the survival of exploit kits) has been steadily dropping over the past few years. This may have forced the attackers to experiment with how viable exploits for other browsers are because they know that sooner or later they will have to make the switch. But judging from these attempts, the attackers do not seem fully capable of making the switch as of now. That is some good news because it could mean that if nothing significant changes, exploit kits might be forced to retire when Internet Explorer usage drops below some critical limit.
CVE-2021-21224
Let’s now take a closer look at the Magnitude’s exploit chain that we discovered in the wild. The exploitation starts with a JavaScript exploit for CVE-2021-21224. This is a type confusion vulnerability in V8, which allows the attacker to execute arbitrary code within a (sandboxed) Chromium renderer process. A zero-day exploit for this vulnerability (or issue 1195777, as it was known back then since no CVE ID had been assigned yet) was dumped on Github on April 14, 2021. The exploit worked for a couple of days against the latest Chrome version, until Google rushed out a patch about a week later.
It should not be surprising that Magnitude’s exploit is heavily inspired by the PoC on Github. However, while both Magnitude’s exploit and the PoC follow a very similar exploitation path, there are no matching code pieces, which suggests that the attackers didn’t resort that much to the “Copy/Paste” technique of exploit development. In fact, Magnitude’s exploit looks like a more cleaned-up and reliable version of the PoC. And since there is no obfuscation employed (the attackers probably meant to add it in later), the exploit is very easy to read and debug. There are even very self-explanatory function names, such as confusion_to_oob, addrof, and arb_write, and variable names, such as oob_array, arb_write_buffer, and oob_array_map_and_properties. The only way this could get any better for us researchers would be if the authors left a couple of helpful comments in there…
Interestingly, some parts of the exploit also seem inspired by a CTF writeup for a “pwn” challenge from *CTF 2019, in which the players were supposed to exploit a made-up vulnerability that was introduced into a fork of V8. While CVE-2021-21224 is obviously a different (and actual rather than made-up) vulnerability, many of the techniques outlined in that writeup apply for V8 exploitation in general and so are used in the later stages of the Magnitude’s exploit, sometimes with the very same variable names as those used in the writeup.
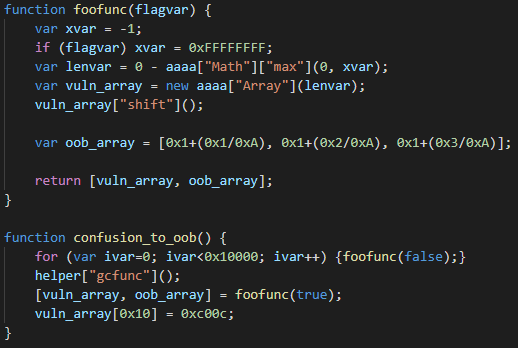
The root cause of the vulnerability is incorrect integer conversion during the SimplifiedLowering phase. This incorrect conversion is triggered in the exploit by the Math.max call, shown in the code snippet above. As can be seen, the exploit first calls foofunc in a loop 0x10000 times. This is to make V8 compile that function because the bug only manifests itself after JIT compilation. Then, helper["gcfunc"] gets called. The purpose of this function is just to trigger garbage collection. We tested that the exploit also works without this call, but the authors probably put it there to improve the exploit’s reliability. Then, foofunc is called one more time, this time with flagvar=true, which makes xvar=0xFFFFFFFF. Without the bug, lenvar should now evaluate to -0xFFFFFFFF and the next statement should throw a RangeError because it should not be possible to create an array with a negative length. However, because of the bug, lenvar evaluates to an unexpected value of 1. The reason for this is that the vulnerable code incorrectly converts the result of Math.max from an unsigned 32-bit integer 0xFFFFFFFF to a signed 32-bit integer -1. After constructing vuln_array, the exploit calls Array.prototype.shift on it. Under normal circumstances, this method should remove the first element from the array, so the length of vuln_array should be zero. However, because of the disparity between the actual and the predicted value of lenvar, V8 makes an incorrect optimization here and just puts the 32-bit constant 0xFFFFFFFF into Array.length (this is computed as 0-1 with an unsigned 32-bit underflow, where 0 is the predicted length and -1 signifies Array.prototype.shift decrementing Array.length).
Now, the attackers have successfully crafted a JSArray with a corrupted Array.length, which allows them to perform out-of-bounds memory reads and writes. The very first out-of-bounds memory write can be seen in the last statement of the confusion_to_oob function. The exploit here writes 0xc00c to vuln_array[0x10]. This abuses the deterministic memory layout in V8 when a function creates two local arrays. Since vuln_array was created first, oob_array is located at a known offset from it in memory and so by making out-of-bounds memory accesses through vuln_array, it is possible to access both the metadata and the actual data of oob_array. In this case, the element at index 0x10 corresponds to offset 0x40, which is where Array.length of oob_array is stored. The out-of-bounds write therefore corrupts the length of oob_array, so it is now too possible to read and write past its end.
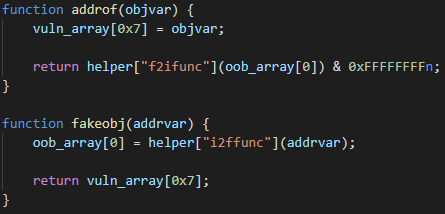
Next, the exploit constructs the addrof and fakeobj exploit primitives. These are well-known and very powerful primitives in the world of JavaScript engine exploitation. In a nutshell, addrof leaks the address of a JavaScript object, while fakeobj creates a new, fake object at a given address. Having constructed these two primitives, the attacker can usually reuse existing techniques to get to their ultimate goal: arbitrary code execution.
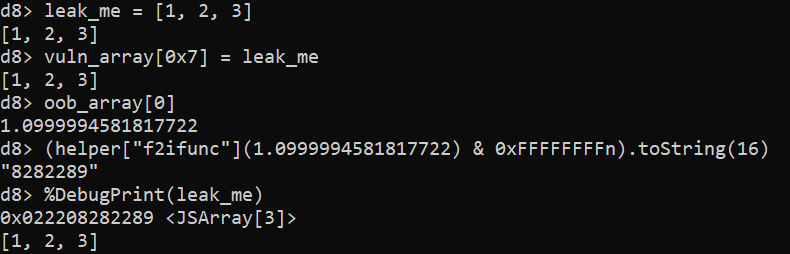
addrof primitive. Note that just the lower 32 bits of the address get leaked, while %DebugPrint returns the whole 64-bit address. In practice, this doesn’t matter because V8 compresses pointers by keeping upper 32 bits of all heap pointers constant.Both primitives are constructed in a similar way, abusing the fact that vuln_array[0x7] and oob_array[0] point to the very same memory location. It is important to note here that vuln_array is internally represented by V8 as HOLEY_ELEMENTS, while oob_array is PACKED_DOUBLE_ELEMENTS (for more information about internal array representation in V8, please refer to this blog post by the V8 devs). This makes it possible to write an object into vuln_array and read it (or more precisely, the pointer to it) from the other end in oob_array as a double. This is exactly how addrof is implemented, as can be seen above. Once the address is read, it is converted using helper["f2ifunc"] from double representation into an integer representation, with the upper 32 bits masked out, because the double takes 64 bits, while pointers in V8 are compressed down to just 32 bits. fakeobj is implemented in the same fashion, just the other way around. First, the pointer is converted into a double using helper["i2ffunc"]. The pointer, encoded as a double, is then written into oob_array[0] and then read from vuln_array[0x7], which tricks V8 into treating it as an actual object. Note that there is no masking needed in fakeobj because the double written into oob_array is represented by more bits than the pointer read from vuln_array.
With addrof and fakeobj in place, the exploit follows a fairly standard exploitation path, which seems heavily inspired by the aforementioned *CTF 2019 writeup. The next primitives constructed by the exploit are arbitrary read/write. To achieve these primitives, the exploit fakes a JSArray (aptly named fake in the code snippet above) in such a way that it has full control over its metadata. It can then overwrite the fake JSArray’s elements pointer, which points to the address where the actual elements of the array get stored. Corrupting the elements pointer allows the attackers to point the fake array to an arbitrary address, and it is then subsequently possible to read/write to that address through reads/writes on the fake array.
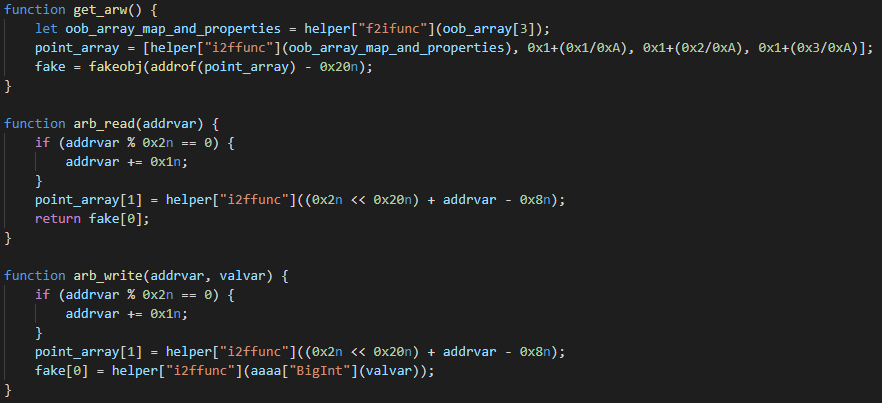
Let’s look at the implementation of the arbitrary read/write primitive in a bit more detail. The exploit first calls the get_arw function to set up the fake JSArray. This function starts by using an overread on oob_array[3] in order to leak map and properties of oob_array (remember that the original length of oob_array was 3 and that its length got corrupted earlier). The map and properties point to structures that basically describe the object type in V8. Then, a new array called point_array gets created, with the oob_array_map_and_properties value as its first element. Finally, the fake JSArray gets constructed at offset 0x20 before point_array. This offset was carefully chosen, so that the the JSArray structure corresponding to fake overlaps with elements of point_array. Therefore, it is possible to control the internal members of fake by modifying the elements of point_array. Note that elements in point_array take 64 bits, while members of the JSArray structure usually only take 32 bits, so modifying one element of point_array might overwrite two members of fake at the same time. Now, it should make sense why the first element of point_array was set to oob_array_map_and_properties. The first element is at the same address where V8 would look for the map and properties of fake. By initializing it like this, fake is created to be a PACKED_DOUBLE_ELEMENTS JSArray, basically inheriting its type from oob_array.
The second element of point_array overlaps with the elements pointer and Array.length of fake. The exploit uses this for both arbitrary read and arbitrary write, first corrupting the elements pointer to point to the desired address and then reading/writing to that address through fake[0]. However, as can be seen in the exploit code above, there are some additional actions taken that are worth explaining. First of all, the exploit always makes sure that addrvar is an odd number. This is because V8 expects pointers to be tagged, with the least significant bit set. Then, there is the addition of 2<<32 to addrvar. As was explained before, the second element of point_array takes up 64 bits in memory, while the elements pointer and Array.length both take up only 32 bits. This means that a write to point_array[1] overwrites both members at once and the 2<<32 just simply sets the Array.length, which is controlled by the most significant 32 bits. Finally, there is the subtraction of 8 from addrvar. This is because the elements pointer does not point straight to the first element, but instead to a FixedDoubleArray structure, which takes up eight bytes and precedes the actual element data in memory.
The final step taken by the exploit is converting the arbitrary read/write primitive into arbitrary code execution. For this, it uses a well-known trick that takes advantage of WebAssembly. When V8 JIT-compiles a WebAssembly function, it places the compiled code into memory pages that are both writable and executable (there now seem to be some new mitigations that aim to prevent this trick, but it is still working against V8 versions vulnerable to CVE-2021-21224). The exploit can therefore locate the code of a JIT-compiled WebAssembly function, overwrite it with its own shellcode and then call the original WebAssembly function from Javascript, which executes the shellcode planted there.
Magnitude’s exploit first creates a dummy WebAssembly module that contains a single function called main, which just returns the number 42 (the original code of this function doesn’t really matter because it will get overwritten with the shellcode anyway). Using a combination of addrof and arb_read, the exploit obtains the address where V8 JIT-compiled the function main. Interestingly, it then constructs a whole new arbitrary write primitive using an ArrayBuffer with a corrupted backing store pointer and uses this newly constructed primitive to write shellcode to the address of main. While it could theoretically use the first arbitrary write primitive to place the shellcode there, it chooses this second method, most likely because it is more reliable. It seems that the first method might crash V8 under some rare circumstances, which makes it not practical for repeated use, such as when it gets called thousands of times to write a large shellcode buffer into memory.
There are two shellcodes embedded in the exploit. The first one contains an exploit for CVE-2021-31956. This one gets executed first and its goal is to steal the SYSTEM token to elevate the privileges of the current process. After the first shellcode returns, the second shellcode gets planted inside the JIT-compiled WebAssembly function and executed. This second shellcode injects Magniber ransomware into some already running process and lets it encrypt the victim’s drives.
CVE-2021-31956
Let’s now turn our attention to the second exploit in the chain, which Magnitude uses to escape the Chromium sandbox. This is an exploit for CVE-2021-31956, a paged pool buffer overflow in the Windows kernel. It was discovered in June 2021 by Boris Larin from Kaspersky, who found it being used as a zero-day in the wild as a part of the PuzzleMaker attack. The Kaspersky blog post about PuzzleMaker briefly describes the vulnerability and the way the attackers chose to exploit it. However, much more information about the vulnerability can be found in a two–part blog series by Alex Plaskett from NCC Group. This blog series goes into great detail and pretty much provides a step-by-step guide on how to exploit the vulnerability. We found that the attackers behind Magnitude followed this guide very closely, even though there are certainly many other approaches that they could have chosen for exploitation. This shows yet again that publishing vulnerability research can be a double-edged sword. While the blog series certainly helped many defend against the vulnerability, it also made it much easier for the attackers to weaponize it.
The vulnerability lies in ntfs.sys, inside the function NtfsQueryEaUserEaList, which is directly reachable from the syscall NtQueryEaFile. This syscall internally allocates a temporary buffer on the paged pool (the size of which is controllable by a syscall parameter) and places there the NTFS Extended Attributes associated with a given file. Individual Extended Attributes are separated by a padding of up to four bytes. By making the padding start directly at the end of the allocated pool chunk, it is possible to trigger an integer underflow which results in NtfsQueryEaUserEaList writing subsequent Extended Attributes past the end of the pool chunk. The idea behind the exploit is to spray the pool so that chunks containing certain Windows Notification Facility (WNF) structures can be corrupted by the overflow. Using some WNF magic that will be explained later, the exploit gains an arbitrary read/write primitive, which it uses to steal the SYSTEM token.
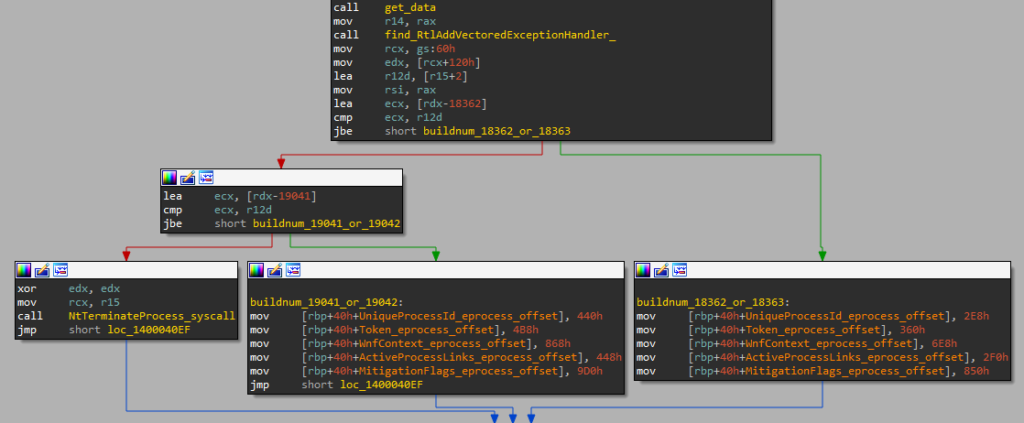
The exploit starts by checking the victim’s Windows build number. Only builds 18362, 18363, 19041, and 19042 (19H1 – 20H2) are supported, and the exploit bails out if it finds itself running on a different build. The build number is then used to determine proper offsets into the _EPROCESS structure as well as to determine correct syscall numbers, because syscalls are invoked directly by the exploit, bypassing the usual syscall stubs in ntdll.
Next, the exploit brute-forces file handles, until it finds one on which it can use the NtSetEAFile syscall to set its NTFS Extended Attributes. Two attributes are set on this file, crafted to trigger an overflow of 0x10 bytes into the next pool chunk later when NtQueryEaFile gets called.
When the specially crafted NTFS Extended Attributes are set, the exploit proceeds to spray the paged pool with _WNF_NAME_INSTANCE and _WNF_STATE_DATA structures. These structures are sprayed using the syscalls NtCreateWnfStateName and NtUpdateWnfStateData, respectively. The exploit then creates 10 000 extra _WNF_STATE_DATA structures in a row and frees each other one using NtDeleteWnfStateData. This creates holes between _WNF_STATE_DATA chunks, which are likely to get reclaimed on future pool allocations of similar size.
With this in mind, the exploit now triggers the vulnerability using NtQueryEaFile, with a high likelihood of getting a pool chunk preceding a random _WNF_STATE_DATA chunk and thus overflowing into that chunk. If that really happens, the _WNF_STATE_DATA structure will get corrupted as shown below. However, the exploit doesn’t know which _WNF_STATE_DATA structure got corrupted, if any. To find the corrupted structure, it has to iterate over all of them and query its ChangeStamp using NtQueryWnfStateData. If the ChangeStamp contains the magic number 0xcafe, the exploit found the corrupted chunk. In case the overflow does not hit any _WNF_STATE_DATA chunk, the exploit just simply tries triggering the vulnerability again, up to 32 times. Note that in case the overflow didn’t hit a _WNF_STATE_DATA chunk, it might have corrupted a random chunk in the paged pool, which could result in a BSoD. However, during our testing of the exploit, we didn’t get any BSoDs during normal exploitation, which suggests that the pool spraying technique used by the attackers is relatively robust.

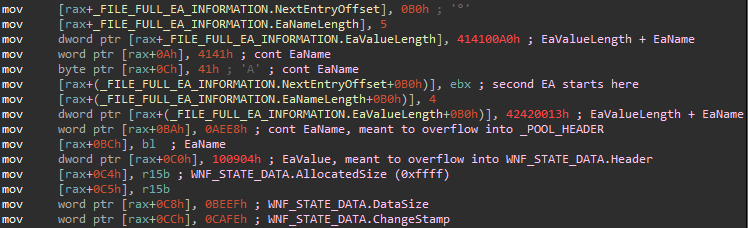
_WNF_STATE_DATA instance. AllocatedSize and DataSize were both artificially increased, while ChangeStamp got set to an easily recognizable value.After a successful _WNF_STATE_DATA corruption, more _WNF_NAME_INSTANCE structures get sprayed on the pool, with the idea that they will reclaim the other chunks freed by NtDeleteWnfStateData. By doing this, the attackers are trying to position a _WNF_NAME_INSTANCE chunk after the corrupted _WNF_STATE_DATA chunk in memory. To explain why they would want this, let’s first discuss what they achieved by corrupting the _WNF_STATE_DATA chunk.
The _WNF_STATE_DATA structure can be thought of as a header preceding an actual WnfStateData buffer in memory. The WnfStateData buffer can be read using the syscall NtQueryWnfStateData and written to using NtUpdateWnfStateData. _WNF_STATE_DATA.AllocatedSize determines how many bytes can be written to WnfStateData and _WNF_STATE_DATA.DataSize determines how many bytes can be read. By corrupting these two fields and setting them to a high value, the exploit gains a relative memory read/write primitive, obtaining the ability to read/write memory even after the original WnfStateData buffer. Now it should be clear why the attackers would want a _WNF_NAME_INSTANCE chunk after a corrupted _WNF_STATE_DATA chunk: they can use the overread/overwrite to have full control over a _WNF_NAME_INSTANCE structure. They just need to perform an overread and scan the overread memory for bytes 03 09 A8, which denote the start of their _WNF_NAME_INSTANCE structure. If they want to change something in this structure, they can just modify some of the overread bytes and overwrite them back using NtUpdateWnfStateData.
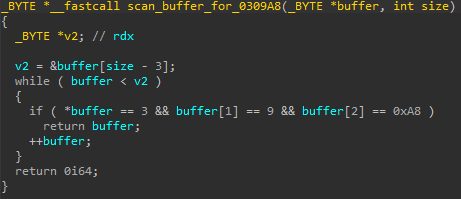
_WNF_NAME_INSTANCE header. 0x0903 here represents the NodeTypeCode, while 0xA8 is a preselected NodeByteSize.What is so interesting about a _WNF_NAME_INSTANCE structure, that the attackers want to have full control over it? Well, first of all, at offset 0x98 there is _WNF_NAME_INSTANCE.CreatorProcess, which gives them a pointer to _EPROCESS relevant to the current process. Kaspersky reported that PuzzleMaker used a separate information disclosure vulnerability, CVE-2021-31955, to leak the _EPROCESS base address. However, the attackers behind Magnitude do not need to use a second vulnerability, because the _EPROCESS address is just there for the taking.
Another important offset is 0x58, which corresponds to _WNF_NAME_INSTANCE.StateData. As the name suggests, this is a pointer to a _WNF_STATE_DATA structure. By modifying this, the attackers can not only enlarge the WnfStateData buffer but also redirect it to an arbitrary address, which gives them an arbitrary read/write primitive. There are some constraints though, such as that the StateData pointer has to point 0x10 bytes before the address that is to be read/written and that there has to be some data there that makes sense when interpreted as a _WNF_STATE_DATA structure.
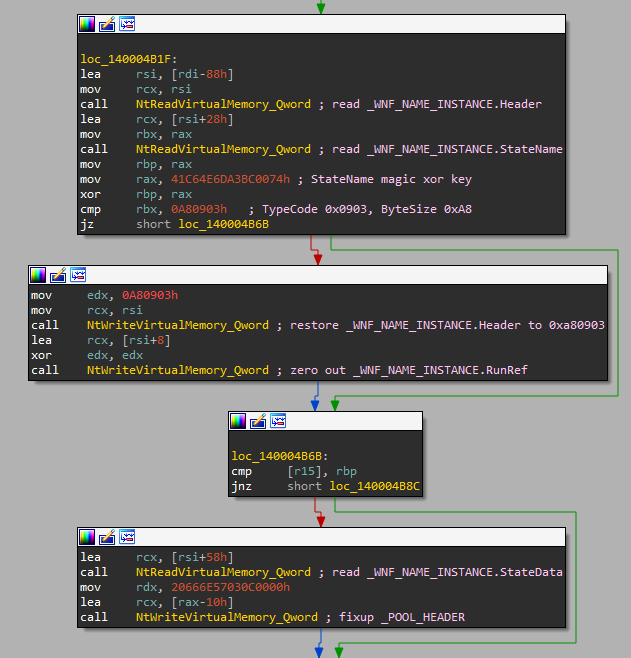
The StateData pointer gets first set to _EPROCESS+0x28, which allows the exploit to read _KPROCESS.ThreadListHead (interestingly, this value gets leaked using ChangeStamp and DataSize, not through WnfStateData). The ThreadListHead points to _KTHREAD.ThreadListEntry of the first thread, which is the current thread in the context of Chromium exploitation. By subtracting the offset of ThreadListEntry, the exploit gets the _KTHREAD base address for the current thread.
With the base address of _KTHREAD, the exploit points StateData to _KTHREAD+0x220, which allows it to read/write up to three bytes starting from _KTHREAD+0x230. It uses this to set the byte at _KTHREAD+0x232 to zero. On the targeted Windows builds, the offset 0x232 corresponds to _KTHREAD.PreviousMode. Setting its value to SystemMode=0 tricks the kernel into believing that some of the thread’s syscalls are actually originating from the kernel. Specifically, this allows the thread to use the NtReadVirtualMemory and NtWriteVirtualMemory syscalls to perform reads and writes to the kernel address space.
As was the case in the Chromium exploit, the attackers here just traded an arbitrary read/write primitive for yet another arbitrary read/write primitive. However, note that the new primitive based on PreviousMode is a significant upgrade compared to the original StateData one. Most importantly, the new primitive is free of the constraints associated with the original one. The new primitive is also more reliable because there are no longer race conditions that could potentially cause a BSoD. Not to mention that just simply calling NtWriteVirtualMemory is much faster and much less awkward than abusing multiple WNF-related syscalls to achieve the same result.
With a robust arbitrary read/write primitive in place, the exploit can finally do its thing and proceed to steal the SYSTEM token. Using the leaked _EPROCESS address from before, it finds _EPROCESS.ActiveProcessLinks, which leads to a linked list of other _EPROCESS structures. It iterates over this list until it finds the System process. Then it reads System’s _EPROCESS.Token and assigns this value (with some of the RefCnt bits masked out) to its own _EPROCESS structure. Finally, the exploit also turns off some mitigation flags in _EPROCESS.MitigationFlags.
Now, the exploit has successfully elevated privileges and can pass control to the other shellcode, which was designed to load Magniber ransomware. But before it does that, the exploit performs many cleanup actions that are necessary to avoid blue screening later on. It iterates over WNF-related structures using TemporaryNamesList from _EPROCESS.WnfContext and fixes all the _WNF_NAME_INSTANCE structures that got overflown into at the beginning of the exploit. It also attempts to fix the _POOL_HEADER of the overflown _WNF_STATE_DATA chunks. Finally, the exploit gets rid of both read/write primitives by setting _KTHREAD.PreviousMode back to UserMode=1 and using one last NtUpdateWnfStateData syscall to restore the corrupted StateData pointer back to its original value.
Final Thoughts
If this isn’t the first time you’re hearing about Magnitude, you might have noticed that it often exploits vulnerabilities that were previously weaponized by APT groups, who used them as zero-days in the wild. To name a few recent examples, CVE-2021-31956 was exploited by PuzzleMaker, CVE-2021-26411 was used in a high-profile attack targeting security researchers, CVE-2020-0986 was abused in Operation Powerfall, and CVE-2019-1367 was reported to be exploited in the wild by an undisclosed threat actor (who might be DarkHotel APT according to Qihoo 360). The fact that the attackers behind Magnitude are so successful in reproducing complex exploits with no public PoCs could lead to some suspicion that they have somehow obtained under-the-counter access to private zero-day exploit samples. After all, we don’t know much about the attackers, but we do know that they are skilled exploit developers, and perhaps Magnitude is not their only source of income. But before we jump to any conclusions, we should mention that there are other, more plausible explanations for why they should prioritize vulnerabilities that were once exploited as zero-days. First, APT groups usually know what they are doing[citation needed]. If an APT group decides that a vulnerability is worth exploiting in the wild, that generally means that the vulnerability is reliably weaponizable. In a way, the attackers behind Magnitude could abuse this to let the APT groups do the hard work of selecting high-quality vulnerabilities for them. Second, zero-days in the wild usually attract a lot of research attention, which means that there are often detailed writeups that analyze the vulnerability’s root cause and speculate about how it could get exploited. These writeups make exploit development a lot easier compared to more obscure vulnerabilities which attracted only a limited amount of research.
As we’ve shown in this blog post, both Magnitude and Underminer managed to successfully develop exploit chains for Chromium on Windows. However, none of the exploit chains were particularly successful in terms of the number of exploited victims. So what does this mean for the future of exploit kits? We believe that unless some new, hard-to-patch vulnerability comes up, exploit kits are not something that the average Google Chrome user should have to worry about much. After all, it has to be acknowledged that Google does a great job at patching and reducing the browser’s attack surface. Unfortunately, the same cannot be said for all other Chromium-based browsers. We found that a big portion of those that we protected from Underminer were running Chromium forks that were months (or even years) behind on patching. Because of this, we recommend avoiding Chromium forks that are slow in applying security patches from the upstream. Also note that some Chromium forks might have vulnerabilities in their own custom codebase. But as long as the number of users running the vulnerable forks is relatively low, exploit kit developers will probably not even bother with implementing exploits specific just for them.
Finally, we should also mention that it is not entirely impossible for exploit kits to attack using zero-day or n-day exploits. If that were to happen, the attackers would probably carry out a massive burst of malvertising or watering hole campaigns. In such a scenario, even regular Google Chrome users would be at risk. The damage done by such an attack could be enormous, depending on the reaction time of browser developers, ad networks, security companies, LEAs, and other concerned parties. There are basically three ways that the attackers could get their hands on a zero-day exploit: they could either buy it, discover it themselves, or discover it being used by some other threat actor. Fortunately, using some simple math we can see that the campaign would have to be very successful if the attackers wanted to recover the cost of the zero-day, which is likely to discourage most of them. Regarding n-day exploitation, it all boils down to a race if the attackers can develop a working exploit sooner than a patch gets written and rolled out to the end users. It’s a hard race to win for the attackers, but it has been won before. We know of at least two cases when an n-day exploit working against the latest Google Chrome version was dumped on GitHub (this probably doesn’t need to be written down, but dumping such exploits on GitHub is not a very bright idea). Fortunately, these were just renderer exploits and there were no accompanying sandbox escape exploits (which would be needed for full weaponization). But if it is possible to win the race for one exploit, it’s not unthinkable that an attacker could win it for two exploits at the same time.
Indicators of Compromise (IoCs)
Magnitude
| SHA-256 | Note |
71179e5677cbdfd8ab85507f90d403afb747fba0e2188b15bd70aac3144ae61a | CVE-2021-21224 exploit |
a7135b92fc8072d0ad9a4d36e81a6b6b78f1528558ef0b19cb51502b50cffe6d | CVE-2021-21224 exploit |
6c7ae2c24eaeed1cac0a35101498d87c914c262f2e0c2cd9350237929d3e1191 | CVE-2021-31956 exploit |
8c52d4a8f76e1604911cff7f6618ffaba330324490156a464a8ceaf9b590b40a | payload injector |
8ff658257649703ee3226c1748bbe9a2d5ab19f9ea640c52fc7d801744299676 | payload injector |
Underminer
| SHA-256 | Note |
2ac255e1e7a93e6709de3bbefbc4e7955af44dbc6f977b60618237282b1fb970 | CVE-2021-21224 exploit |
9552e0819f24deeea876ba3e7d5eff2d215ce0d3e1f043095a6b1db70327a3d2 | HiddenBee loader |
7a3ba9b9905f3e59e99b107e329980ea1c562a5522f5c8f362340473ebf2ac6d | HiddenBee module container |
2595f4607fad7be0a36cb328345a18f344be0c89ab2f98d1828d4154d68365f8 | amd64/coredll.bin |
ed7e6318efa905f71614987942a94df56fd0e17c63d035738daf97895e8182ab | amd64/pcs.bin |
c2c51aa8317286c79c4d012952015c382420e4d9049914c367d6e72d81185494 | CVE-2019-0808 exploit |
d88371c41fc25c723b4706719090f5c8b93aad30f762f62f2afcd09dd3089169 | CVE-2020-1020 exploit |
b201fd9a3622aff0b0d64e829c9d838b5f150a9b20a600e087602b5cdb11e7d3 | CVE-2020-1054 exploit |